LONDON: When two shells exploded 100 meters from Al-Nau Hospital in the Sudanese city of Omdurman last week, medical staff felt the explosion and feared the worst.
A few days earlier, a blast at a busy market nearby killed 54 people and injured 158. Medics had battled to treat the dozens of bloodied casualties brought through the doors.
This time the explosions killed six people, including a hospital volunteer.
Even within the devastation of Sudan’s war, two such deadly attacks taking place within days of each other shocked those working at the hospital.

The shelling came amid an escalation in fighting across the heavily populated Khartoum state as the Sudanese army (SAF) and its allies attempt to retake full control of the capital from the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) militia.
If successful, it would be a victory that reshapes the conflict but, analysts say, is unlikely to bring it to an end.
Jean-Nicolas Armstrong Dangelser, Sudan emergency coordinator for the charity Doctors Without Borders (MSF), was in Al-Nau Hospital’s emergency room at the time of the two attacks.
“The map of the conflict is changing literally by the hour,” he told Arab News. “It’s obviously coming with a big increase of violence, because there is fighting now spreading on multiple front lines.
“The hospital staff are seeing the direct impact of the conflict with the war wounded coming in and a lot of civilians being affected.”
The market attack and shelling near Al-Nau Hospital was blamed on the RSF as it rapidly withdraws from greater Khartoum, which includes Omdurman.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
When the war broke out in April 2023 as part of a power struggle between Gen. Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, SAF’s leader and Sudan’s de-facto ruler, and RSF commander Mohammed Hamdan Dagalo, the militia seized control of much of Khartoum, along with large swaths of the vast country.
The military-led government relocated to Port Sudan as fighting raged, killing tens of thousands of people, displacing almost 12 million and leading to famine in several parts of the country.
Late last year, SAF mounted a comeback after sourcing more weapons, including drones, and carrying out a recruitment drive. After months of fighting, there was a major breakthrough in January when they seized Wad Madani, the capital of Al-Jazirah state.
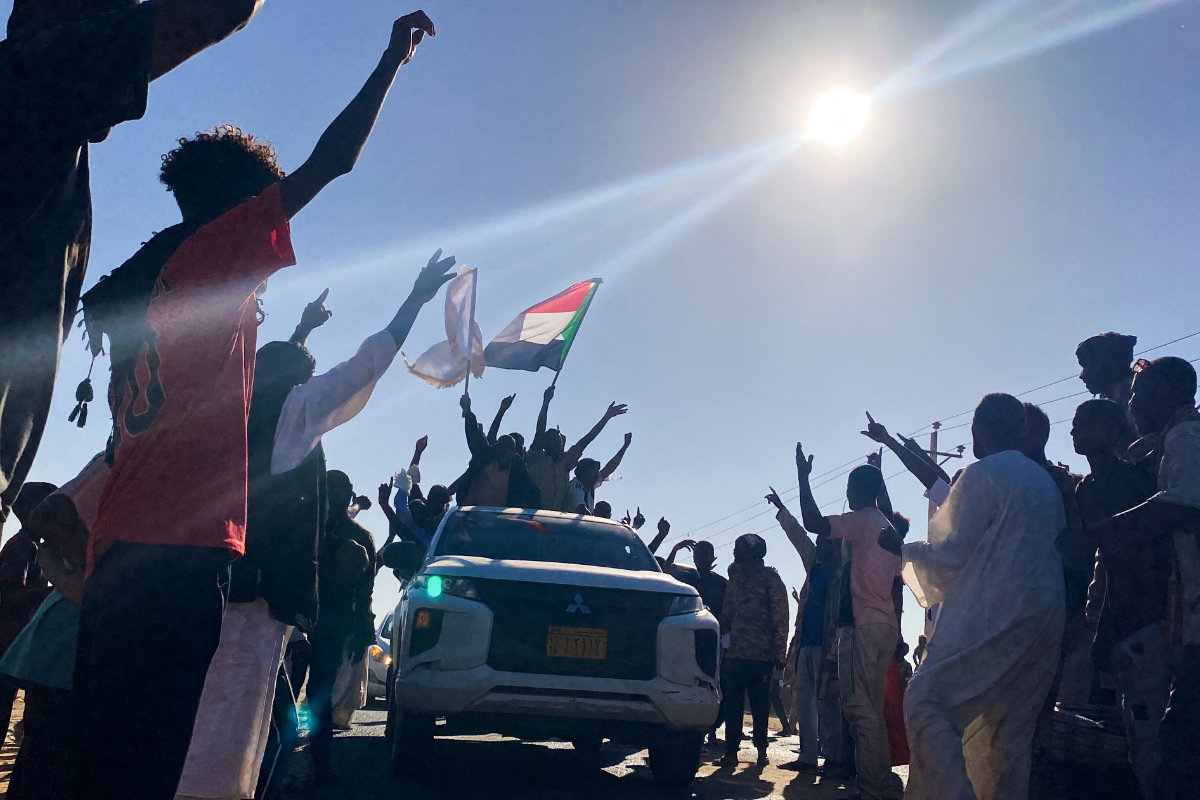

Sudanese people celebrate with passengers of passing vehicles in Meroe in the country's Northern State on January 11, 2025, after the army announced entering key Al-Jazira state capital Wad Madani, held by the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces. (AFP)
Since then, the army has launched offensives from multiple directions into the outskirts of Khartoum, getting the upper hand in the adjacent cities of Omdurman and Khartoum North, also known as Bahri, which make up greater Khartoum.
On Friday, the army said it had retaken Kafouri district in Khartoum North, an important base for the RSF in what would be one of its most significant defeats so far.
The expulsion of RSF fighters from Wad Madani was followed by allegations of summary executions and reprisals against those accused by SAF soldiers of being RSF informants or collaborators. These reports are a cause for concern for Khartoum residents who have lived through months of RSF control over their neighborhoods.
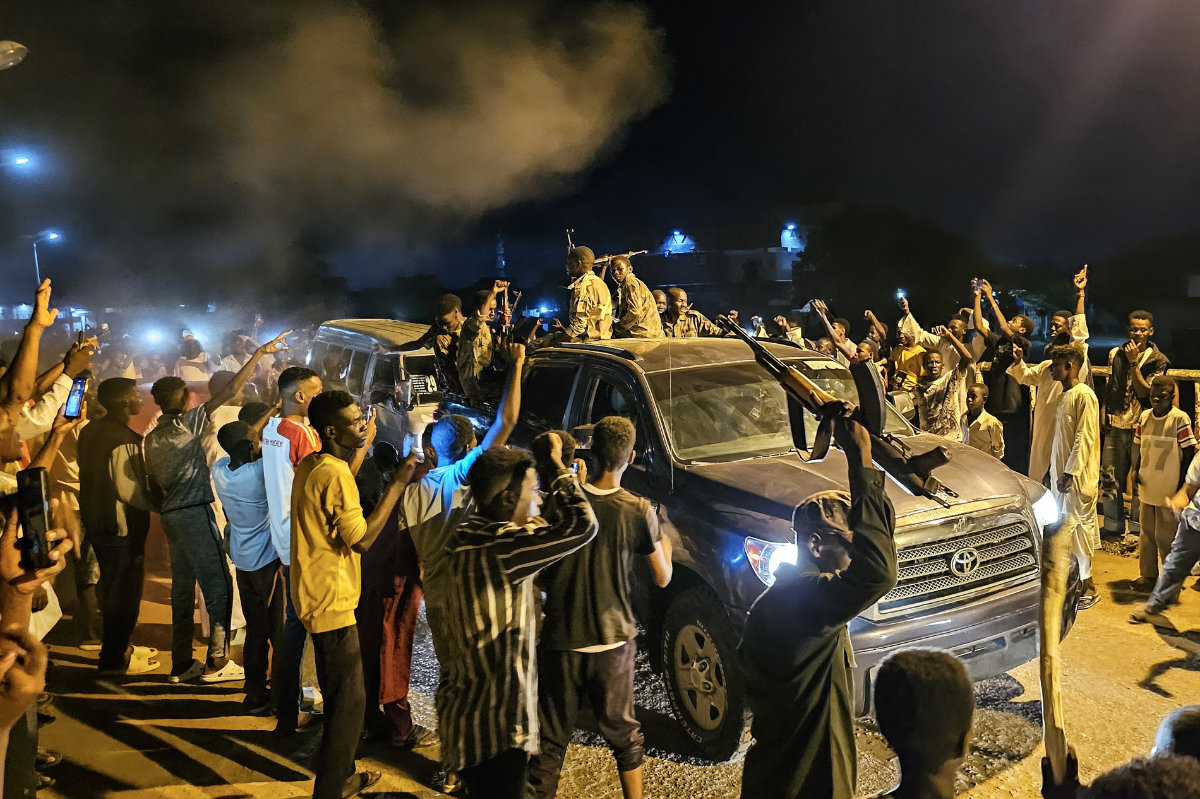
Caption
Retaking the whole of Khartoum seems inevitable and would undoubtedly be a major symbolic and strategic victory for the army.
But hope that it may usher in an end to the conflict, either militarily through a defeat of the RSF or through a negotiated settlement, remains highly unlikely.
The RSF still holds sway in much of western Sudan, which includes the Darfur region, where Dagalo and many of his fighters come from.
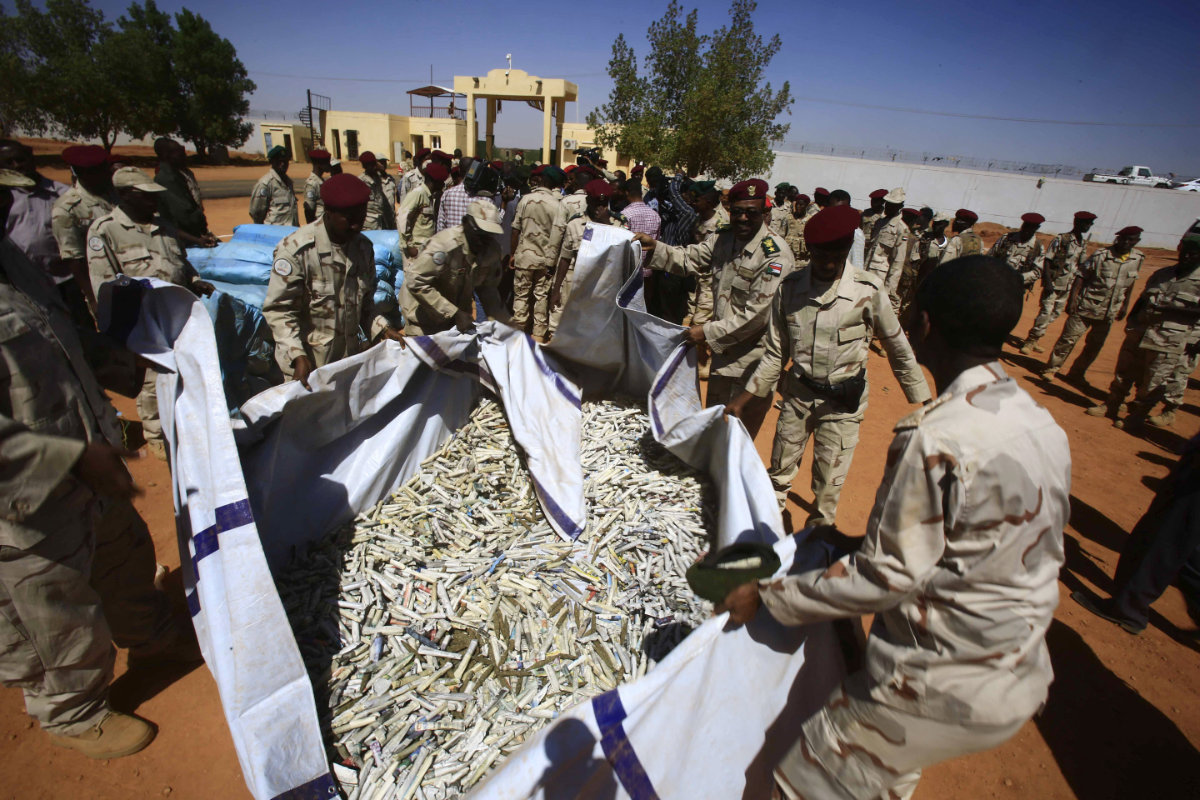

In this November 5, 2017 photo, General Mohammed Dagalo's Rapid Support Forces display sacks of hashish that they captured in the state of South Darfur a week earlier by ambushing a gang of smugglers that was transporting the drugs to Khartoum. (AFP)
Ahmed Soliman, a senior research fellow at international affairs think tank Chatham House, says the RSF’s full retreat from Khartoum would not mean that the militia had been defeated.
“It would be a significant setback for the RSF, but we have to keep that in context also to what the RSF has been able to do during this war, which is to capture very substantial amounts of territory,” he told Arab News.
The RSF controls four of the five states in Darfur and has ramped up its siege of El-Fasher, the capital of North Darfur. It also controls gold mines in other parts of Darfur and holds large parts of the Kordofan region.
“The RSF is very focused also on maintaining supply lines to the border areas with South Sudan, particularly the southwest,” Soliman added.
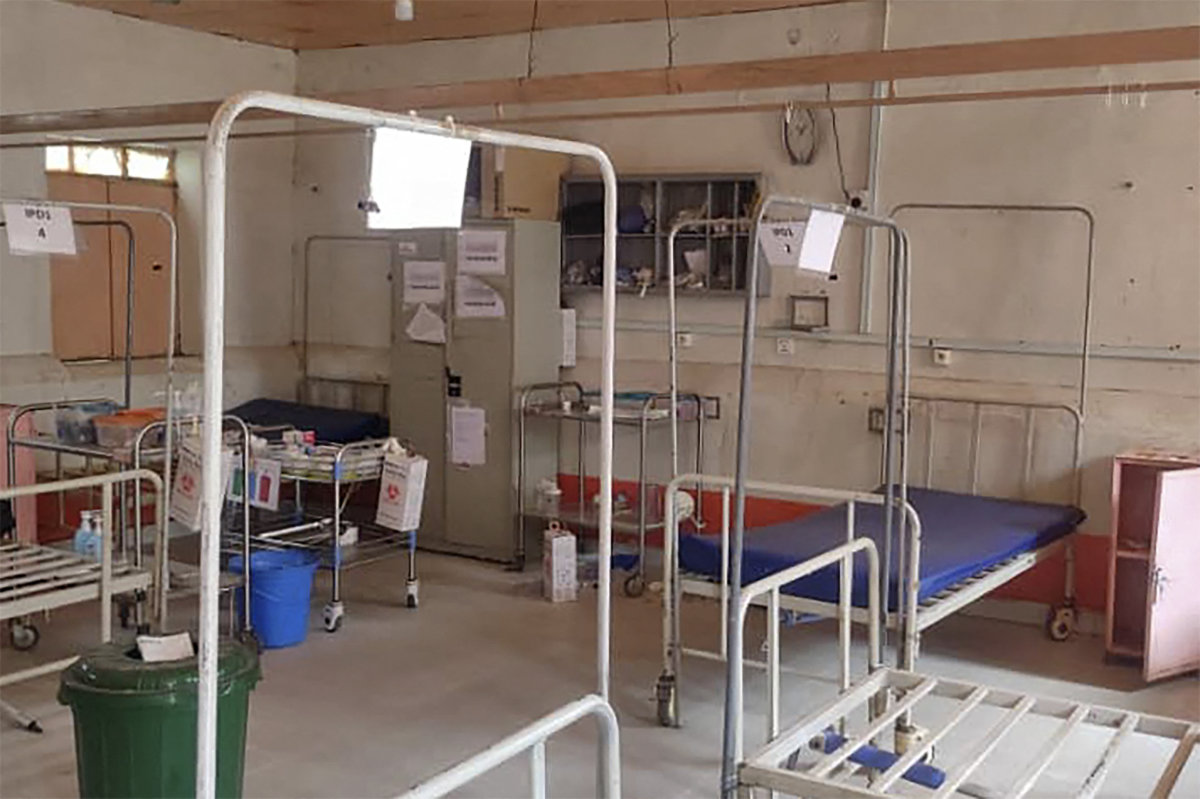

A picture taken on May 1, 2023 shows an abandoned hospital in El Geneina, the capital of West Darfur, as deadly fighting continued in Sudan between rival generals' forces. (AFP/File)
If the army can consolidate power in Khartoum, it is unsure whether there would be enough incentive for the RSF to enter ceasefire talks given the “substantial amounts of territory and resources” it controls.
Even without a truce, taking the capital would certainly change the dynamics of the conflict along with the calculations of the two sides, Soliman said.
For the military and its supporters, which include the political elites from the regime of deposed President Omar Bashir, reinstating the government in Khartoum may feel like “mission accomplished” in the conflict.
That would still leave the RSF in control of huge areas and effectively lead to a fragmented Sudan with different regions of de-facto governance, Soliman added.
“The preservation of Sudanese unity may be at stake,” he said.
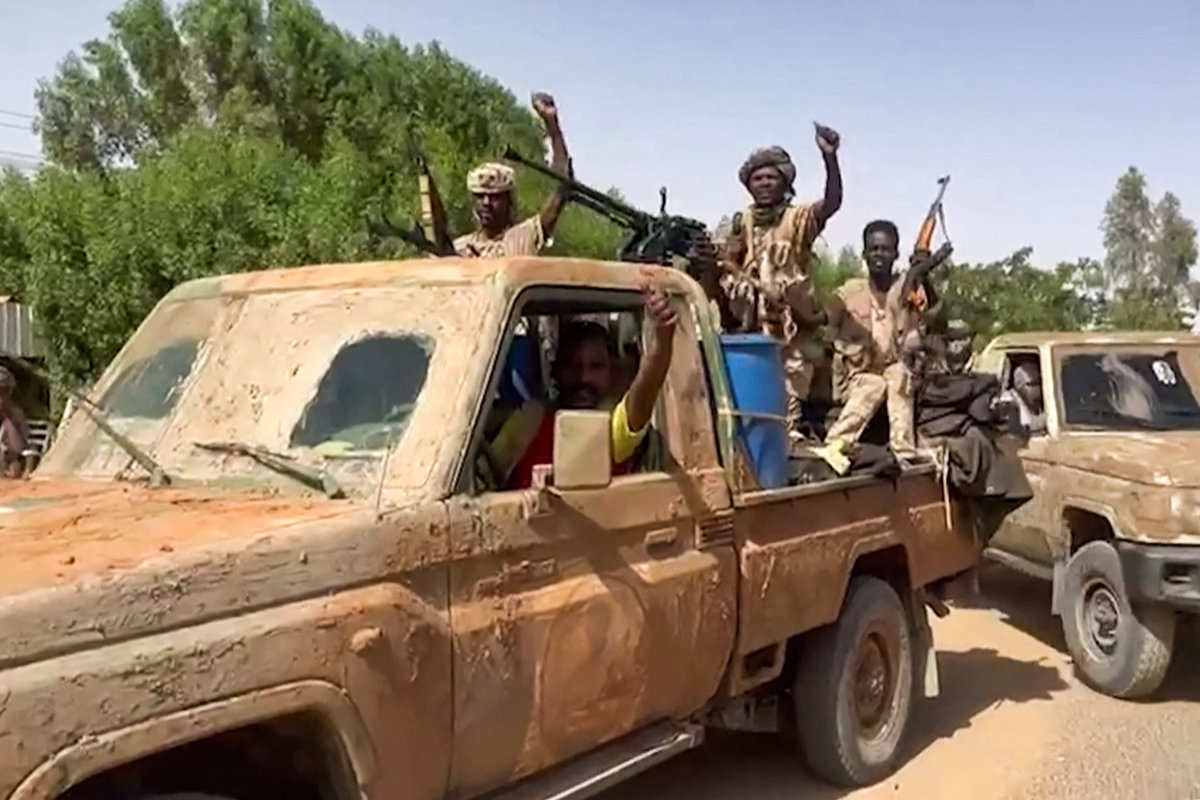

Despite being ousted from the capital, Khartoum, General Mohammed Dagalo's Rapid Support Forces still hold sway in much of western Sudan, which includes the Darfur region, where Dagalo and many of his fighters come from. (AFP)
A clue as to how the military’s retaking of Khartoum might affect Sudan’s future came on Saturday when Burhan announced plans to form a transitional government.
He said the administration’s main objective would be to “accomplish the remaining military tasks … and cleanse all of Sudan” of the RSF, AFP news agency reported. It would also prepare for a broader political transition and eventually elections.
While the uncertainty over the direction of the conflict will do little to reassure Sudanese over their futures, the recapturing of areas near Khartoum has allowed some to return to their homes or gain access to medical help.
Over the weekend, MSF assisted the health ministry to set up mobile clinics in North Khartoum in areas recently retaken by the army.
Populations there have spent nearly two years struggling to find food, clean water and medicine, Armstrong Dangelser said.
Their condition, however, is evidence of the suffering the conflict has inflicted.
The MSF-supported hospitals are dealing with injuries related to shelling and airstrikes, but there are also the health effects of people living without clean water to wash and drink, no electricity and a lack of food.
INNUMBERS
• 10,000+ People suffering from famine in Khartoum alone.
• 12m+ People displaced by Sudan’s conflict since April 2023.
• 28,700+ Conflict’s death toll as per ACLED records.
They have dealt with cholera outbreaks and other diseases associated with not having access to basic services, and malnutrition is rife.
Disturbingly, Armstrong Dangelser said they had recently seen a surge in stabbing wounds and close-range gunshots, something he associated with outbreaks of looting as the RSF flees the areas they controlled.
There have also been widespread reports of reprisal killings in areas taken over by the army. The violence is in keeping with the level of brutality meted out by the two sides throughout the war.
The US accused the RSF last month of committing genocide and placed sanctions on its leader, Dagalo, who is known as “Hemedti.” Washington also sanctioned Al-Burhan for killing civilians and targeting schools and hospitals.
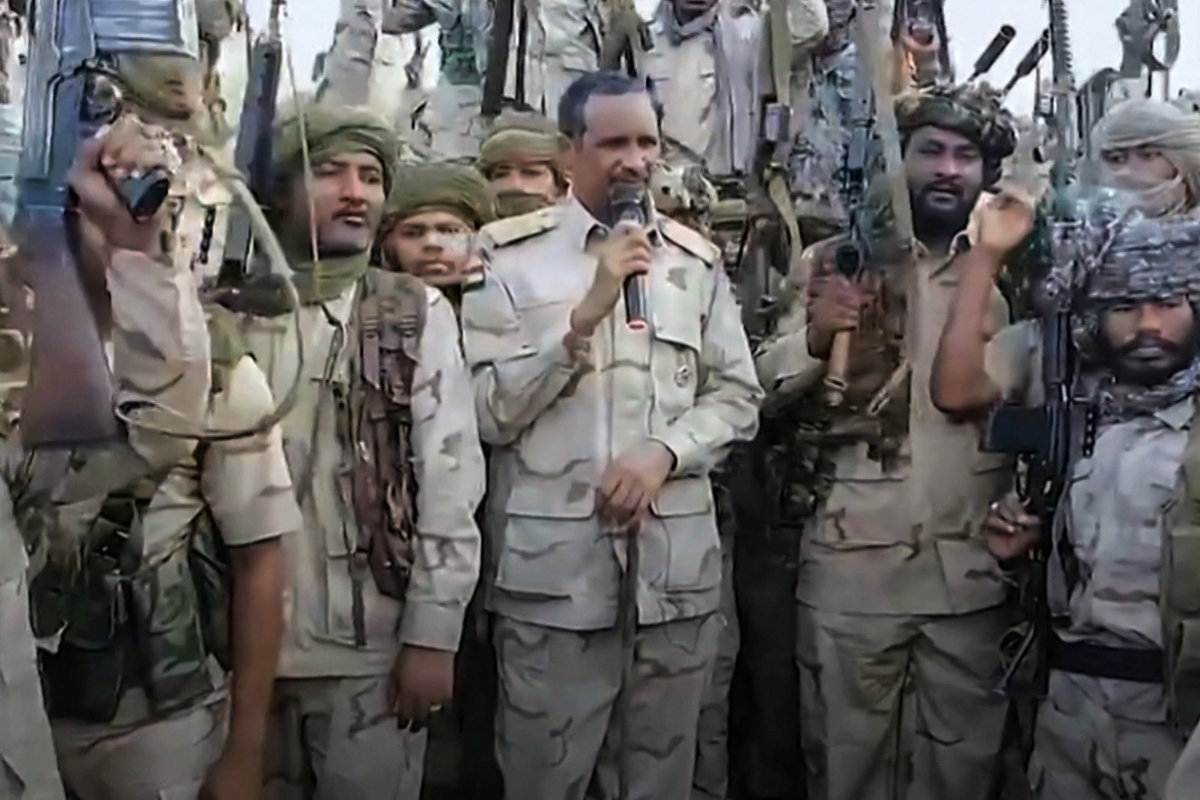

An image grab taken from a handout video posted on the Sudanese paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) page on X on July 28, 2023 shows its commander Mohamed Hamdan Daglo addressing RSF fighters at an undisclosed location. (AFP/File)
Al-Burhan and Dagalo led a coup together in October 2021 that overthrew a transitional government before the two men fell out spectacularly and led the country into war.
This latest phase has led to a sharp rise in civilian deaths, the UN said on Friday, with 275 civilians killed between Jan. 31 and Feb. 5 by shelling and airstrikes.
For aid workers dealing with the world’s worst humanitarian disaster, a new front has also emerged in recent weeks — President Donald Trump’s decision to suspend foreign aid.
As of September, the US had provided nearly $2 billion to the emergency response in Sudan since the conflict started, making it by far the biggest provider of aid to the country.
"What we are seeing now with the US funding cuts is truly devastating for a lot of people," Armstrong Dangelser said.
Whatever direction the conflict takes next, the suffering of the Sudanese is set to continue.































